We have an array arr[]. We need to find the sum of all the elements in the range L and R where 0 <= L <= R <= n-1. Consider a situation when there are many range queries.
Examples:
Input : 3 7 2 5 8 9
query(0, 5)
query(3, 5)
query(2, 4)
Output : 34
22
15
Note : array is 0 based indexed
and queries too.
Since there are no updates/modifications, we use the Sparse table to answer queries efficiently. In a sparse table, we break queries in powers of 2.
Suppose we are asked to compute sum of
elements from arr[i] to arr[i+12].
We do the following:
// Use sum of 8 (or 23) elements
table[i][3] = sum(arr[i], arr[i + 1], ...
arr[i + 7]).
// Use sum of 4 elements
table[i+8][2] = sum(arr[i+8], arr[i+9], ..
arr[i+11]).
// Use sum of single element
table[i + 12][0] = sum(arr[i + 12]).
Our result is sum of above values.
Notice that it took only 4 actions to compute the result over a subarray of size 13.
Flowchart:
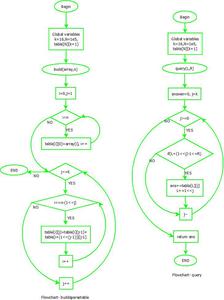
Flowchart
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int k = 16;
const int N = 1e5;
long long table[N][k + 1];
void buildSparseTable(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
table[i][0] = arr[i];
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
for (int i = 0; i <= n - (1 << j); i++)
table[i][j] = table[i][j - 1] +
table[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1];
}
long long query(int L, int R)
{
long long answer = 0;
for (int j = k; j >= 0; j--) {
if (L + (1 << j) - 1 <= R) {
answer = answer + table[L][j];
L += 1 << j;
}
}
return answer;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 7, 2, 5, 8, 9 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
buildSparseTable(arr, n);
cout << query(0, 5) << endl;
cout << query(3, 5) << endl;
cout << query(2, 4) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG
{
static int k = 16;
static int N = 100000;
static long table[][] = new long[N][k + 1];
static void buildSparseTable(int arr[],
int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
table[i][0] = arr[i];
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
for (int i = 0; i <= n - (1 << j); i++)
table[i][j] = table[i][j - 1] +
table[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1];
}
static long query(int L, int R)
{
long answer = 0;
for (int j = k; j >= 0; j--)
{
if (L + (1 << j) - 1 <= R)
{
answer = answer + table[L][j];
L += 1 << j;
}
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 3, 7, 2, 5, 8, 9 };
int n = arr.length;
buildSparseTable(arr, n);
System.out.println(query(0, 5));
System.out.println(query(3, 5));
System.out.println(query(2, 4));
}
}
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int k = 16;
static int N = 100000;
static long [,]table =
new long[N, k + 1];
static void buildSparseTable(int []arr,
int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
table[i, 0] = arr[i];
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
for (int i = 0;
i <= n - (1 << j); i++)
table[i, j] = table[i, j - 1] +
table[i + (1 << (j - 1)), j - 1];
}
static long query(int L, int R)
{
long answer = 0;
for (int j = k; j >= 0; j--)
{
if (L + (1 << j) - 1 <= R)
{
answer = answer +
table[L, j];
L += 1 << j;
}
}
return answer;
}
static void Main()
{
int []arr = new int[]{3, 7, 2,
5, 8, 9};
int n = arr.Length;
buildSparseTable(arr, n);
Console.WriteLine(query(0, 5));
Console.WriteLine(query(3, 5));
Console.WriteLine(query(2, 4));
}
}
|
Python3
k = 16
n = 100000
table = [[0 for j in range(k+1)] for i in range(n)]
def buildSparseTable(arr, n):
global table, k
for i in range(n):
table[i][0] = arr[i]
for j in range(1,k+1):
for i in range(0,n-(1<<j)+1):
table[i][j] = table[i][j-1] + \
table[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1]
def query(L, R):
global table, k
answer = 0
for j in range(k,-1,-1):
if (L + (1 << j) - 1 <= R):
answer = answer + table[L][j]
L+=1<<j
return answer
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [3, 7, 2, 5, 8, 9]
n = len(arr)
buildSparseTable(arr, n)
print(query(0,5))
print(query(3,5))
print(query(2,4))
|
Javascript
<script>
const k = 16;
const N = 1e5;
const table = new Array(N).fill(0).map(() => new Array(k + 1).fill(0));
function buildSparseTable(arr, n)
{
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
table[i][0] = arr[i];
for (let j = 1; j <= k; j++)
for (let i = 0; i <= n - (1 << j); i++)
table[i][j] = table[i][j - 1] +
table[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1];
}
function query(L, R)
{
let answer = 0;
for (let j = k; j >= 0; j--)
{
if (L + (1 << j) - 1 <= R)
{
answer = answer + table[L][j];
L += 1 << j;
}
}
return answer;
}
let arr = [ 3, 7, 2, 5, 8, 9 ];
let n = arr.length;
buildSparseTable(arr, n);
document.write(query(0, 5) + "<br>");
document.write(query(3, 5) + "<br>");
document.write(query(2, 4) + "<br>");
</script>
|
Output:
34
22
15
This algorithm for answering queries with Sparse Table works in O(k), which is O(log(n)) because we choose minimal k such that 2^k+1 > n.
Time complexity of sparse table construction : Outer loop runs in O(k), inner loop runs in O(n). Thus, in total we get O(n * k) = O(n * log(n))
Auxiliary Space: O(n*k), since n*k extra space has been taken.
Feeling lost in the world of random DSA topics, wasting time without progress? It's time for a change! Join our DSA course, where we'll guide you on an exciting journey to master DSA efficiently and on schedule.
Ready to dive in? Explore our Free Demo Content and join our DSA course, trusted by over 100,000 geeks!