Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm that works similar to the way you sort playing cards in your hands. The array is virtually split into a sorted and an unsorted part. Values from the unsorted part are picked and placed at the correct position in the sorted part.
Insertion Sort Algorithm
To sort an array of size N in ascending order iterate over the array and compare the current element (key) to its predecessor, if the key element is smaller than its predecessor, compare it to the elements before. Move the greater elements one position up to make space for the swapped element.
Working of Insertion Sort algorithm
Consider an example: arr[]: {12, 11, 13, 5, 6}
First Pass:
- Initially, the first two elements of the array are compared in insertion sort.
- Here, 12 is greater than 11 hence they are not in the ascending order and 12 is not at its correct position. Thus, swap 11 and 12.
- So, for now 11 is stored in a sorted sub-array.
Second Pass:
- Now, move to the next two elements and compare them
- Here, 13 is greater than 12, thus both elements seems to be in ascending order, hence, no swapping will occur. 12 also stored in a sorted sub-array along with 11
Third Pass:
- Now, two elements are present in the sorted sub-array which are 11 and 12
- Moving forward to the next two elements which are 13 and 5
- Both 5 and 13 are not present at their correct place so swap them
- After swapping, elements 12 and 5 are not sorted, thus swap again
- Here, again 11 and 5 are not sorted, hence swap again
- Here, 5 is at its correct position
Fourth Pass:
- Now, the elements which are present in the sorted sub-array are 5, 11 and 12
- Moving to the next two elements 13 and 6
- Clearly, they are not sorted, thus perform swap between both
- Now, 6 is smaller than 12, hence, swap again
- Here, also swapping makes 11 and 6 unsorted hence, swap again
- Finally, the array is completely sorted.
Illustrations:
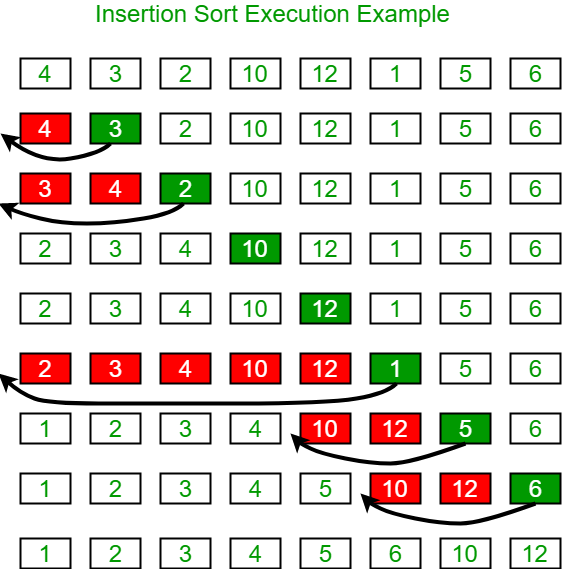
Implementation of Insertion Sort Algorithm
Below is the implementation of the iterative approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void insertionSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, key, j;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
key = arr[i];
j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j = j - 1;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
insertionSort(arr, N);
printArray(arr, N);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void insertionSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, key, j;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
key = arr[i];
j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j = j - 1;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
insertionSort(arr, n);
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
public class InsertionSort {
void sort(int arr[])
{
int n = arr.length;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int key = arr[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j = j - 1;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
static void printArray(int arr[])
{
int n = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 };
InsertionSort ob = new InsertionSort();
ob.sort(arr);
printArray(arr);
}
};
|
Python
def insertionSort(arr):
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
key = arr[i]
j = i-1
while j >= 0 and key < arr[j] :
arr[j + 1] = arr[j]
j -= 1
arr[j + 1] = key
arr = [12, 11, 13, 5, 6]
insertionSort(arr)
for i in range(len(arr)):
print ("% d" % arr[i])
|
C#
using System;
class InsertionSort {
void sort(int[] arr)
{
int n = arr.Length;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int key = arr[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j = j - 1;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
static void printArray(int[] arr)
{
int n = arr.Length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
Console.Write("\n");
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 };
InsertionSort ob = new InsertionSort();
ob.sort(arr);
printArray(arr);
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function insertionSort(&$arr, $n)
{
for ($i = 1; $i < $n; $i++)
{
$key = $arr[$i];
$j = $i-1;
while ($j >= 0 && $arr[$j] > $key)
{
$arr[$j + 1] = $arr[$j];
$j = $j - 1;
}
$arr[$j + 1] = $key;
}
}
function printArray(&$arr, $n)
{
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
echo $arr[$i]." ";
echo "\n";
}
$arr = array(12, 11, 13, 5, 6);
$n = sizeof($arr);
insertionSort($arr, $n);
printArray($arr, $n);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function insertionSort(arr, n)
{
let i, key, j;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
key = arr[i];
j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key)
{
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j = j - 1;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
function printArray(arr, n)
{
let i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
document.write(arr[i] + " ");
document.write("<br>");
}
let arr = [12, 11, 13, 5, 6 ];
let n = arr.length;
insertionSort(arr, n);
printArray(arr, n);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N^2)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Complexity Analysis of Insertion Sort:
Time Complexity of Insertion Sort
- The worst-case time complexity of the Insertion sort is O(N^2)
- The average case time complexity of the Insertion sort is O(N^2)
- The time complexity of the best case is O(N).
Space Complexity of Insertion Sort
The auxiliary space complexity of Insertion Sort is O(1)
Characteristics of Insertion Sort
- This algorithm is one of the simplest algorithms with a simple implementation
- Basically, Insertion sort is efficient for small data values
- Insertion sort is adaptive in nature, i.e. it is appropriate for data sets that are already partially sorted.
Frequently Asked Questions on Insertion Sort
Q1. What are the Boundary Cases of the Insertion Sort algorithm?
Insertion sort takes the maximum time to sort if elements are sorted in reverse order. And it takes minimum time (Order of n) when elements are already sorted.
Q2. What is the Algorithmic Paradigm of the Insertion Sort algorithm?
The Insertion Sort algorithm follows an incremental approach.
Q3. Is Insertion Sort an in-place sorting algorithm?
Yes, insertion sort is an in-place sorting algorithm.
Q4. Is Insertion Sort a stable algorithm?
Yes, insertion sort is a stable sorting algorithm.
Q5. When is the Insertion Sort algorithm used?
Insertion sort is used when number of elements is small. It can also be useful when the input array is almost sorted, and only a few elements are misplaced in a complete big array.
Feeling lost in the world of random DSA topics, wasting time without progress? It's time for a change! Join our DSA course, where we'll guide you on an exciting journey to master DSA efficiently and on schedule.
Ready to dive in? Explore our Free Demo Content and join our DSA course, trusted by over 100,000 geeks!