Given an array of integers, find the length of the longest sub-sequence such that elements in the subsequence are consecutive integers, the consecutive numbers can be in any order.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = {1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2}
Output: 4
Explanation: The subsequence 1, 3, 4, 2 is the longest subsequence of consecutive elements
Input: arr[] = {36, 41, 56, 35, 44, 33, 34, 92, 43, 32, 42}
Output: 5
Explanation: The subsequence 36, 35, 33, 34, 32 is the longest subsequence of consecutive elements.
Naive Approach:
The idea is to first sort the array and find the longest subarray with consecutive elements. After sorting the array and removing the multiple occurrences of elements, run a loop and keep a count and max (both initially zero). Run a loop from start to end and if the current element is not equal to the previous (element+1) then set the count to 1 else increase the count. Update max with a maximum of count and max.
Illustration:
Input: arr[] = {1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2}
First sort the array to arrange them in a consecutive fashion.
arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 9, 10, 20}
Now, store the distinct elements from the sorted array.
dist[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 9, 10, 20}
Initialize countConsecutive with 0 which will increment when arr[i] == arr[i – 1] + 1 is true otherwise countConsecutive will re-initialize by 1.
Maintain a variable ans to store the maximum count of consecutive elements so far.
At i = 0:
- as i is 0 then re-initialize countConsecutive by 1.
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = max(0, 1) = 1
At i = 1:
- check if (dist[1] == dist[0] + 1) = (2 == 1 + 1) = true
- as the above condition is true, therefore increment countConsecutive by 1
- countConsecutive = countConsecutive + 1 = 1 + 1 = 2
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = max(1, 2) = 1
At i = 2:
- check if (dist[2] == dist[1] + 1) = (3 == 2 + 1) = true
- as the above condition is true, therefore increment countConsecutive by 1
- countConsecutive = countConsecutive + 1 = 2 + 1 = 3
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = max(2, 3) = 3
At i = 3:
- check if (dist[3] == dist[2] + 1) = (4 == 3 + 1) = true
- as the above condition is true, therefore increment countConsecutive by 1
- countConsecutive = countConsecutive + 1 = 3 + 1 = 4
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = max(3, 4) = 4
At i = 4:
- check if (dist[4] == dist[3] + 1) = (9 != 4 + 1) = false
- as the above condition is false, therefore re-initialize countConsecutive by 1
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = max(4, 1) = 4
At i = 5:
- check if (dist[5] == dist[4] + 1) = (10 == 9 + 1) = true
- as the above condition is true, therefore increment countConsecutive by 1
- countConsecutive = countConsecutive + 1 = 1 + 1 = 2
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = max(4, 2) = 4
At i = 6:
- check if (dist[6] == dist[5] + 1) = (20 != 10 + 1) = false
- as the above condition is false, therefore re-initialize countConsecutive by 1
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = max(4, 1) = 4
Therefore the longest consecutive subsequence is {1, 2, 3, 4}
Hence, ans is 4.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Initialize ans and countConsecutive with 0.
- Sort the arr[].
- Store the distinct elements in dist[] array by traversing over the arr[].
- Now, traverse on the dist[] array to find the count of consecutive elements.
- Simultaneously maintain the answer variable.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int findLongestConseqSubseq(int arr[], int n)
{
int ans = 0, count = 0;
sort(arr, arr + n);
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(arr[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] != arr[i - 1])
v.push_back(arr[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
if (i > 0 && v[i] == v[i - 1] + 1)
count++;
else
count = 1;
ans = max(ans, count);
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 2, 3 };
int n = sizeof arr / sizeof arr[0];
cout << "Length of the Longest contiguous subsequence "
"is "
<< findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int findLongestConseqSubseq(int arr[], int n)
{
Arrays.sort(arr);
int ans = 0, count = 0;
ArrayList<Integer> v = new ArrayList<Integer>();
v.add(arr[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] != arr[i - 1])
v.add(arr[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
if (i > 0 && v.get(i) == v.get(i - 1) + 1)
count++;
else
count = 1;
ans = Math.max(ans, count);
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println(
"Length of the Longest "
+ "contiguous subsequence is "
+ findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n));
}
}
|
Python3
def findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n):
ans = 0
count = 0
arr.sort()
v = []
v.append(arr[0])
for i in range(1, n):
if (arr[i] != arr[i - 1]):
v.append(arr[i])
for i in range(len(v)):
if (i > 0 and v[i] == v[i - 1] + 1):
count += 1
else:
count = 1
ans = max(ans, count)
return ans
arr = [1, 2, 2, 3]
n = len(arr)
print("Length of the Longest contiguous subsequence is",
findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
static int findLongestConseqSubseq(int[] arr, int n)
{
Array.Sort(arr);
int ans = 0, count = 0;
List<int> v = new List<int>();
v.Add(10);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] != arr[i - 1])
v.Add(arr[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < v.Count; i++) {
if (i > 0 && v[i] == v[i - 1] + 1)
count++;
else
count = 1;
ans = Math.Max(ans, count);
}
return ans;
}
static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(
"Length of the Longest "
+ "contiguous subsequence is "
+ findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n) {
let ans = 0, count = 0;
arr.sort(function (a, b) { return a - b; })
var v = [];
v.push(arr[0]);
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] != arr[i - 1])
v.push(arr[i]);
}
for (let i = 0; i < v.length; i++) {
if (i > 0 && v[i] == v[i - 1] + 1)
count++;
else
count = 1;
ans = Math.max(ans, count);
}
return ans;
}
let arr = [1, 2, 2, 3];
let n = arr.length;
document.write(
"Length of the Longest contiguous subsequence is "
+findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n)
);
</script>
|
Output
Length of the Longest contiguous subsequence is 3
Time complexity: O(Nlog(N)), Time to sort the array is O(Nlog(N)).
Auxiliary space: O(N). Extra space is needed for storing distinct elements.
Longest Consecutive Subsequence using sorting without removing duplicate elements:
The approach involves initially sorting the array. Next, you count the consecutive elements present in the sorted array while skipping any repeated elements.
Below is the implementation:
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
int main()
{
int arr[] = {0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3};
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
if (N == 1)
{
std::cout << "Longest Consecutive subsequence: 1" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
std::sort(arr, arr + N);
int count = 1;
int max_count = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++)
{
if (arr[i + 1] - arr[i] == 1)
{
count++;
}
else if (arr[i + 1] - arr[i] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
count = 1;
}
max_count = std::max(max_count, count);
}
std::cout << "Longest Consecutive subsequence: " << max_count << std::endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = {0,1,1,1,1,1,2,3};
int N = arr.length;
if(N == 1){
System.out.println("Longest Consecutive subsequence: 1");
return;
}
Arrays.sort(arr);
int count = 1;
int max_count = -1;
for(int i=0; i < N-1; i++)
{
if(arr[i+1] - arr[i] == 1)
{
count++;
}
else if(arr[i+1] - arr[i] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
count = 1;
}
max_count = Math.max(max_count, count);
}
System.out.println("Longest Consecutive subsequence: "+max_count);
}
}
|
Python
def find_longest_contiguous_subsequence(arr):
arr.sort()
n = len(arr)
if n == 1:
return 1
count = 1
max_count = -1
for i in range(n - 1):
if arr[i + 1] - arr[i] == 1:
count += 1
elif arr[i + 1] - arr[i] == 0:
continue
else:
count = 1
max_count = max(max_count, count)
return max_count
arr = [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3]
result = find_longest_contiguous_subsequence(arr)
print("Longest Consecutive subsequence:", result)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Linq;
namespace LongestConsecutiveSubsequence
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3 };
int N = arr.Length;
if (N == 1)
{
Console.WriteLine("Longest Consecutive subsequence: 1");
return;
}
Array.Sort(arr);
int count = 1;
int maxCount = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++)
{
if (arr[i + 1] - arr[i] == 1)
{
count++;
}
else if (arr[i + 1] - arr[i] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
count = 1;
}
maxCount = Math.Max(maxCount, count);
}
Console.WriteLine($"Longest Consecutive subsequence: {maxCount}");
}
}
}
|
Javascript
function findLongestConsecutiveSubsequence(arr) {
let N = arr.length;
if (N === 1) {
console.log("Longest Consecutive subsequence: 1");
return;
}
arr.sort((a, b) => a - b);
let count = 1;
let max_count = -1;
for (let i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
if (arr[i + 1] - arr[i] === 1) {
count++;
}
else if (arr[i + 1] - arr[i] === 0) {
continue;
}
else {
count = 1;
}
max_count = Math.max(max_count, count);
}
console.log("Longest Consecutive subsequence: " + max_count);
}
let arr = [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3];
findLongestConsecutiveSubsequence(arr);
|
Output
Longest Consecutive subsequence: 4
Time Complexity: O(NlogN): Due to the sorting step, while the subsequent traversal of the sorted array only requires O(N) time.
Space Complexity: O(1): No extra space is being used.
Longest Consecutive Subsequence using Hashing:
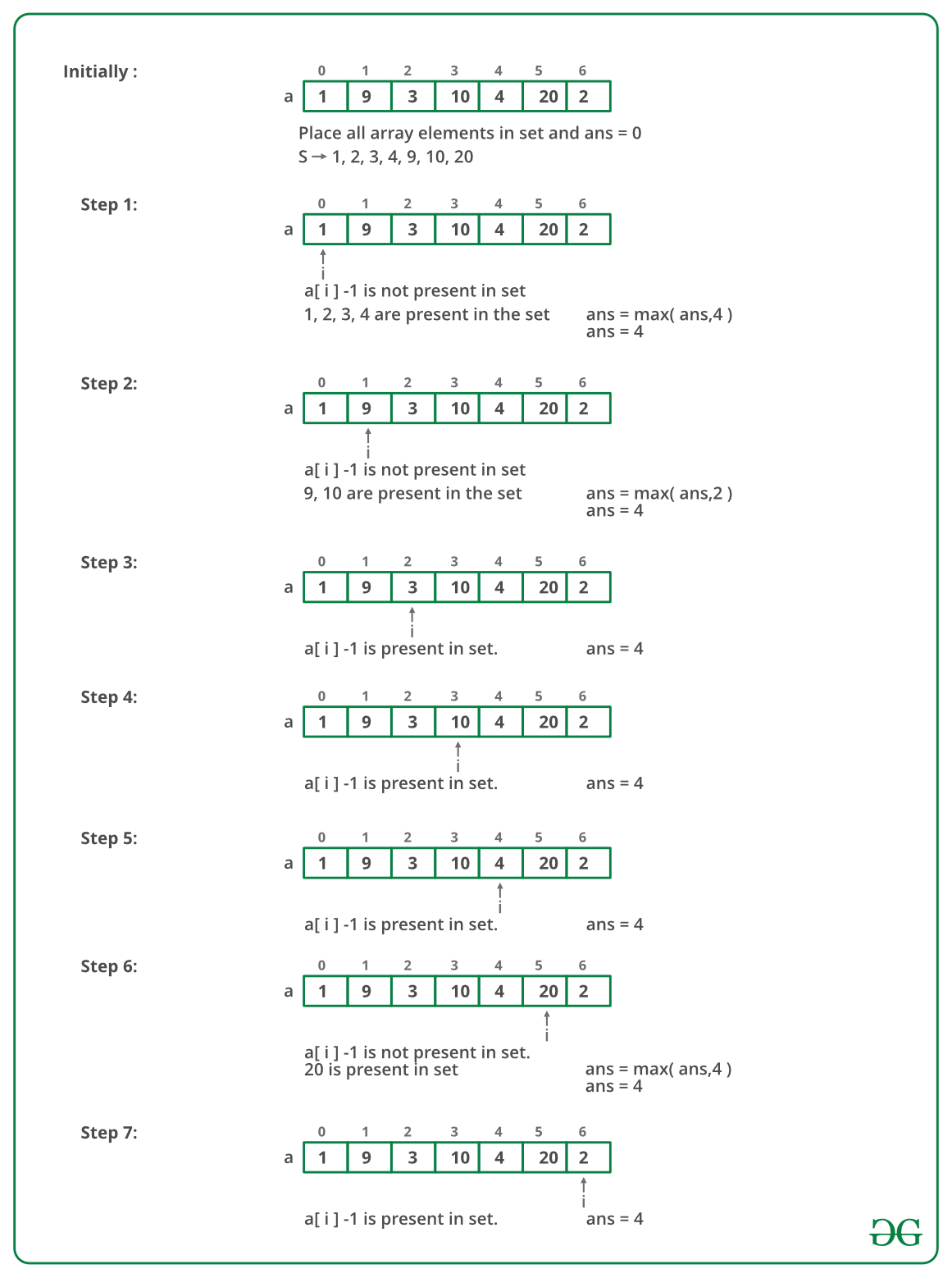
The idea is to use Hashing. We first insert all elements in a Set. Then check all the possible starts of consecutive subsequences.
Illustration:
Below image is the dry run, for example, arr[] = {1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2}:
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Create an empty hash.
- Insert all array elements to hash.
- Do the following for every element arr[i]
- Check if this element is the starting point of a subsequence. To check this, simply look for arr[i] – 1 in the hash, if not found, then this is the first element of a subsequence.
- If this element is the first element, then count the number of elements in the consecutive starting with this element. Iterate from arr[i] + 1 till the last element that can be found.
- If the count is more than the previous longest subsequence found, then update this.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int findLongestConseqSubseq(int arr[], int n)
{
unordered_set<int> S;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
S.insert(arr[i]);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (S.find(arr[i] - 1) != S.end()) {
continue;
}
else {
int j = arr[i];
while (S.find(j) != S.end())
j++;
ans = max(ans, j - arr[i]);
}
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = sizeof arr / sizeof arr[0];
cout << "Length of the Longest contiguous subsequence "
"is "
<< findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class ArrayElements {
static int findLongestConseqSubseq(int arr[], int n)
{
HashSet<Integer> S = new HashSet<Integer>();
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
S.add(arr[i]);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (!S.contains(arr[i] - 1)) {
int j = arr[i];
while (S.contains(j)){
S.remove(Integer.valueOf(j));
j++;
}
if (ans < j - arr[i])
ans = j - arr[i];
}
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println(
"Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is "
+ findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n));
}
}
|
Python3
def findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n):
s = set()
ans = 0
for ele in arr:
s.add(ele)
for i in range(n):
if (arr[i]-1) not in s:
j = arr[i]
while(j in s):
j += 1
ans = max(ans, j-arr[i])
return ans
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 7
arr = [1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2]
print("Length of the Longest contiguous subsequence is ",
findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class ArrayElements {
public static int findLongestConseqSubseq(int[] arr,
int n)
{
HashSet<int> S = new HashSet<int>();
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
S.Add(arr[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (!S.Contains(arr[i] - 1)) {
int j = arr[i];
while (S.Contains(j)) {
j++;
}
if (ans < j - arr[i]) {
ans = j - arr[i];
}
}
}
return ans;
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arr = new int[] { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(
"Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is "
+ findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n) {
let S = new Set();
let ans = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
S.add(arr[i]);
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (!S.has(arr[i] - 1))
{
let j = arr[i];
while (S.has(j))
j++;
ans = Math.max(ans, j - arr[i]);
}
}
return ans;
}
let arr = [1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2];
let n = arr.length;
document.write("Length of the Longest contiguous subsequence is "
+ findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n));
</script>
|
Output
Length of the Longest contiguous subsequence is 4
Time complexity: O(N), Only one traversal is needed and the time complexity is O(n) under the assumption that hash insert and search takes O(1) time.
Auxiliary space: O(N), To store every element in the hashmap O(n) space is needed
Longest Consecutive Subsequence using Priority Queue:
The Idea is to use Priority Queue. Using priority queue it will sort the elements and eventually it will help to find consecutive elements.
Illustration:
Input: arr[] = {1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2}
Insert all the elements in the Priority Queue:
Initialise variable prev with first element of priority queue, prev will contain last element has been picked and it will help to check whether the current element is contributing for consecutive sequence or not.
prev = 1, countConsecutive = 1, ans = 1
Run the algorithm till the priority queue becomes empty.
- current element is 2
- prev + 1 == 2, therefore increment countConsecutive by 1
- countConsecutive = countConsecutive + 1 = 1 + 1 = 2
- update prev with current element, prev = 2
- pop the current element
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = (1, 2) = 2
- current element is 3
- prev + 1 == 3, therefore increment countConsecutive by 1
- countConsecutive = countConsecutive + 1 = 2 + 1 = 3
- update prev with current element, prev = 3
- pop the current element
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = (2, 3) = 3
- current element is 4
- prev + 1 == 4, therefore increment countConsecutive by 1
- countConsecutive = countConsecutive + 1 = 3 + 1 = 4
- update prev with current element, prev = 4
- pop the current element
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = (3, 4) = 4
- current element is 9
- prev + 1 != 9, therefore re-initialise countConsecutive by 1
- countConsecutive = 1
- update prev with current element, prev = 9
- pop the current element
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = (4, 1) = 4
- current element is 10
- prev + 1 == 10, therefore increment countConsecutive by 1
- countConsecutive = countConsecutive + 1 = 1 + 1 = 2
- update prev with current element, prev = 10
- pop the current element
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = (4, 2) =4
- current element is 20
- prev + 1 != 20, therefore re-initialise countConsecutive by 1
- countConsecutive = 1
- update prev with current element, prev = 20
- pop the current element
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = (4, 1) = 4
Hence, the longest consecutive subsequence is 4.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Create a Priority Queue to store the element
- Store the first element in a variable
- Remove it from the Priority Queue
- Check the difference between this removed first element and the new peek element
- If the difference is equal to 1 increase the count by 1 and repeats step 2 and step 3
- If the difference is greater than 1 set counter to 1 and repeat step 2 and step 3
- if the difference is equal to 0 repeat step 2 and 3
- if counter greater than the previous maximum then store counter to maximum
- Continue step 4 to 7 until we reach the end of the Priority Queue
- Return the maximum value
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int findLongestConseqSubseq(int arr[], int N)
{
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > pq;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
pq.push(arr[i]);
}
int prev = pq.top();
pq.pop();
int c = 1;
int max = 1;
while (!pq.empty()) {
if (pq.top() - prev > 1) {
c = 1;
prev = pq.top();
pq.pop();
}
else if (pq.top() - prev == 0) {
prev = pq.top();
pq.pop();
}
else {
c++;
prev = pq.top();
pq.pop();
}
if (max < c) {
max = c;
}
}
return max;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = 7;
cout << "Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence "
"is "
<< findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Longset_Sub {
static int findLongestConseqSubseq(int arr[], int N)
{
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq
= new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
pq.add(arr[i]);
}
int prev = pq.poll();
int c = 1;
int max = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
if (pq.peek() - prev > 1) {
c = 1;
prev = pq.poll();
}
else if (pq.peek() - prev == 0) {
prev = pq.poll();
}
else {
c++;
prev = pq.poll();
}
if (max < c) {
max = c;
}
}
return max;
}
public static void main(String args[])
throws IOException
{
int arr[] = { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println(
"Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is "
+ findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n));
}
}
|
Python3
import bisect
def findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, N):
pq = []
for i in range(N):
bisect.insort(pq, arr[i])
prev = pq[0]
pq.pop(0)
c = 1
max = 1
while(len(pq)):
if(pq[0] - prev > 1):
c = 1
prev = pq[0]
pq.pop(0)
elif(pq[0] - prev == 0):
prev = pq[0]
pq.pop(0)
else:
c = c + 1
prev = pq[0]
pq.pop(0)
if(max < c):
max = c
return max
arr = [1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2]
n = 7
print("Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is {}".format(
findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n)))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
static int findLongestConseqSubseq(int[] arr, int N)
{
List<int> pq = new List<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
pq.Add(arr[i]);
pq.Sort();
}
int prev = pq[0];
int c = 1;
int max = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
if (pq[0] - prev > 1) {
c = 1;
prev = pq[0];
pq.RemoveAt(0);
}
else if (pq[0] - prev == 0) {
prev = pq[0];
pq.RemoveAt(0);
}
else {
c++;
prev = pq[0];
pq.RemoveAt(0);
}
if (max < c) {
max = c;
}
}
return max;
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(
"Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is "
+ findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n));
}
}
|
Javascript
function findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, N) {
let pq = new PriorityQueue();
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
pq.push(arr[i]);
}
let prev = pq.poll();
let c = 1;
let max = 1;
for (let i = 1; i < N; i++) {
if (pq.peek() - prev > 1) {
c = 1;
prev = pq.poll();
} else if (pq.peek() - prev == 0) {
prev = pq.poll();
} else {
c++;
prev = pq.poll();
}
if (max < c) {
max = c;
}
}
return max;
}
class PriorityQueue {
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
push(element) {
this.items.push(element);
this.bubbleUp(this.items.length - 1);
}
peek() {
if (this.items.length === 0) {
return null;
}
return this.items[0];
}
poll() {
if (this.items.length === 0) {
return null;
}
const root = this.items[0];
const last = this.items.pop();
if (this.items.length > 0) {
this.items[0] = last;
this.bubbleDown(0);
}
return root;
}
bubbleUp(index) {
while (index > 0) {
const parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
if (this.items[parentIndex] <= this.items[index]) {
break;
}
const temp = this.items[parentIndex];
this.items[parentIndex] = this.items[index];
this.items[index] = temp;
index = parentIndex;
}
}
bubbleDown(index) {
while (true) {
const leftChildIndex = 2 * index + 1;
const rightChildIndex = 2 * index + 2;
let smallestChildIndex = index;
if (
leftChildIndex < this.items.length &&
this.items[leftChildIndex] < this.items[smallestChildIndex]
) {
smallestChildIndex = leftChildIndex;
}
if (
rightChildIndex < this.items.length &&
this.items[rightChildIndex] < this.items[smallestChildIndex]
) {
smallestChildIndex = rightChildIndex;
}
if (smallestChildIndex === index) {
break;
}
const temp = this.items[smallestChildIndex];
this.items[smallestChildIndex] = this.items[index];
this.items[index] = temp;
index = smallestChildIndex;
}
}
}
const arr = [1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2];
const n = arr.length;
console.log(
"Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is " +
findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n)
);
|
Output
Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is 4
Time Complexity: O(N*log(N)), Time required to push and pop N elements is logN for each element.
Auxiliary Space: O(N), Space required by priority queue to store N elements.
Longest Consecutive Subsequence using Dynamic Programming:
For each number in the input array find the longest possible consecutive sequence starting at that number
For e.g. if input is [3, 2, 1], find the longest possible sequence starting with 3, 2, 1. Each time you find the longest possible sequence
memoize the sequence length for future use.
For e.g. once you find the longest possible sequence starting with 3, of length 1 (since there is no other number after 3) and you need to find the longest sequence starting at 2, you do not need to recalculate the length of sequence starting with 3 as you have solved this sub-problem before. So you can reuse the memoized value.
To solve this problem, we store the current consecutive count in dp[i].
When we have a sorted array: [1, 3, 4, 4, 5], the output is 3. So we want dp[i] to remains unchanged when sorted[i] equals to sorted[i-1], in this case dp is [1, 1, 2, 2, 3].
And we reset dp[i] to 1 if sorted[i] – sorted[i-1] is not equals to 0 or 1.
Sort the array to make sure the number is in ascending order.
Initialize the parameters
max = 0
dp[0] = 1
Loop through the sorted array
If sorted[i] – sorted[i-1] equals to 1 => dp[i] = dp[i-1] + 1 and update max if dp[i] > original max
else if sorted[i] – sorted[i-1] equals to 0 => dp[i] = 1
else dp[i] = 1
Return the maximum.
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int dfs(int start, unordered_map<int, int>& longest);
int longestConsecutive(vector<int>& nums) {
if (nums.size() <= 1) {
return nums.size();
}
int max = 1;
unordered_map<int, int> longest;
for (int n : nums) {
longest[n] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
max = std::max(max, dfs(nums[i], longest));
}
return max;
}
int dfs(int start, unordered_map<int, int>& longest) {
if (longest.find(start) == longest.end()) {
return 0;
}
if (longest[start] != 0) {
return longest[start];
}
int currentLongest = 1 + dfs(start + 1, longest);
longest[start] = currentLongest;
return currentLongest;
}
int main() {
vector<int> arr = {1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2};
cout << "Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is "
<< longestConsecutive(arr) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Longset_Sub {
public static int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length <= 1) {
return nums.length;
}
int max = 1;
Map<Integer, Integer> longest = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int n : nums) {
longest.put(n, null);
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, dfs(nums[i], longest));
}
return max;
}
private static int dfs(int start, Map<Integer, Integer> longest) {
if (!longest.containsKey(start)) {
return 0;
}
if (longest.get(start) != null) {
return longest.get(start);
}
int currentLongest = 1 + dfs(start + 1, longest);
longest.put(start, currentLongest);
return currentLongest;
}
public static void main(String args[])
throws IOException
{
int arr[] = { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println(
"Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is "
+ longestConsecutive(arr));
}
}
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class LongestConsecutiveSequence
{
static int Dfs(int start, Dictionary<int, int> longest)
{
if (!longest.ContainsKey(start))
{
return 0;
}
if (longest[start] != 0)
{
return longest[start];
}
int currentLongest = 1 + Dfs(start + 1, longest);
longest[start] = currentLongest;
return currentLongest;
}
static int LongestConsecutive(int[] nums)
{
if (nums.Length <= 1)
{
return nums.Length;
}
int max = 1;
Dictionary<int, int> longest = new Dictionary<int, int>();
foreach (int n in nums)
{
longest[n] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)
{
max = Math.Max(max, Dfs(nums[i], longest));
}
return max;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
Console.WriteLine("Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is " + LongestConsecutive(arr));
}
}
|
Output
Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is 4
Time complexity: O(N), Only one traversal is needed and the time complexity is O(n) under the assumption that hash insert and search takes O(1) time.
Auxiliary space: O(N), To store every element in the hashmap O(n) space is needed.
Feeling lost in the world of random DSA topics, wasting time without progress? It's time for a change! Join our DSA course, where we'll guide you on an exciting journey to master DSA efficiently and on schedule.
Ready to dive in? Explore our Free Demo Content and join our DSA course, trusted by over 100,000 geeks!