An array is a linear data structure. In an array, the operation to fetch a value takes constant time i.e., O(1). Let us see why is it so.
Why the complexity of fetching value is O(1)?
As Arrays are allocated contiguously in memory, Fetching a value via an index of the array is an arithmetic operation. All arithmetic operations are done in constant time i.e., O(1).
Explanation:
In an array, we have the memory address of index 0 (Base address). By adding the product of the index number (of value to be fetched) and the size of one element (ex. int size is 4 bytes) with the base address, we can have the address of that index’s value. we don’t have to iterate through the array. So it’s done in O(1).
Address of ith Index = Base address + offset = Address of 0th Index + i × (size of one element)
Example:
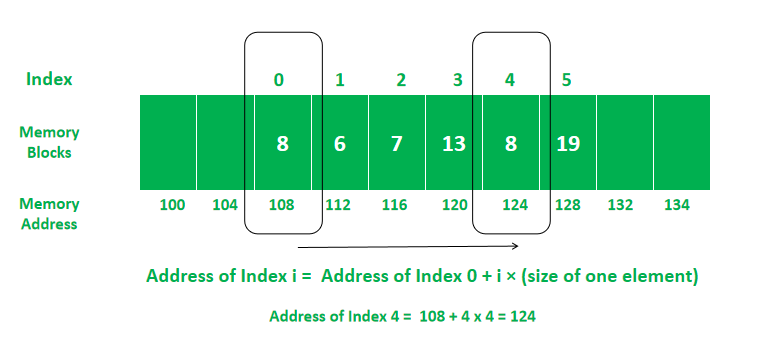
Memory Allocation In Array
In array A[] = {8, 6, 7, 13, 8, 19}
To fetch the value at index 4, we need the memory address where the value of that index is stored. The address can be obtained by doing an arithmetic operation i.e.
Address of value at index 4 = Address of index 0’s value + 4 × size of int = 108 + 4 × 4 bytes
Address of value at index 4 = 124
A[4] = value at address 124 = 8
For more details, please refer:
Design and Analysis of Algorithms.
Feeling lost in the world of random DSA topics, wasting time without progress? It's time for a change! Join our DSA course, where we'll guide you on an exciting journey to master DSA efficiently and on schedule.
Ready to dive in? Explore our Free Demo Content and join our DSA course, trusted by over 100,000 geeks!